好的,没有问题。我将为您不遗漏地、缓慢逐步地详细解释这份名为“UN3079 RECITATION 7”的文档,从头到尾涵盖每个部分的所有内容和全部细节。我会添加详细的解释、具体的数值示例,并按照您的要求为标题添加连续编号,使用Markdown格式标记公式和物理化学名词。
1. 标题和课程信息
## UN3079 RECITATION 7
## Recitation: Mondays 9am (Havemeyer 711) & 6pm (Havemeyer 320)
TA: Lauren Schaffer (she/they); E-mail: 1ks2160@columbia.edu
Office Hour: Tuesdays 5:30-6:30pm, Havemeyer 7th Floor.
详细解释
这部分是文档的抬头,提供了基本的课程管理信息。
- UN3079 RECITATION 7: 这表明该文档是哥伦比亚大学课程编号为 "UN3079" 的第七次习题课(Recitation)的讲义。习题课通常是伴随主课程(Lecture)的小班讨论课,由助教(TA)主持,旨在帮助学生更好地理解课程内容、解决疑难问题和完成作业。
- Recitation 时间和地点:
- 星期一上午9点,在 Havemeyer Hall 的711教室。
- 星期一晚上6点,在 Havemeyer Hall 的320教室。
- 这说明为了方便不同时间安排的学生,该课程提供了两个相同内容的习题课时间段。
- 助教 (TA) 信息:
- 姓名: Lauren Schaffer。
- 代词: she/they,这表示了助教希望被称呼的代词,体现了对性别认同的尊重。
- 电子邮件: lks2160@columbia.edu,这是学生联系助教的主要方式。
- 答疑时间 (Office Hour): 星期二下午5:30到6:30,在 Havemeyer Hall 的七楼。这是学生可以与助教进行一对一或小组交流,提问问题和寻求帮助的固定时间。
2. 第一部分:溶液 I:液-液溶液 (第24章)
## I. Solutions I: Liquid-Liquid Solutions (Chapter 24)
We move on to describing the thermodynamics of liquid-liquid solutions. Perhaps most importantly we will meet the Gibbs-Duhem equation, which relates the change in the properties of one component of a solution in terms of the change in the properties of the other component. Just like how we had ideal gases, our simplest model of a solution we will use is called an "ideal solution," which obeys Raoult's law over the entire composition range.
详细解释
这部分是本次习题课主题的引言,介绍了即将讨论的核心概念。
- 液-液溶液 (Liquid-Liquid Solutions): 这是本次讨论的物理系统,即由两种或多种可互溶的液体混合而成的均一相。
- 热力学描述 (Thermodynamics): 我们的目标是运用热力学的原理和函数(如吉布斯自由能、化学势等)来描述和预测这些溶液的行为。
- 吉布斯-杜亥姆方程 (Gibbs-Duhem equation): 这是本章的一个核心内容。文档强调了它的重要性:它建立了一个数学关系,说明了在多组分体系中,一个组分性质的变化必然会引起另一个组分性质的相应变化。它们不是相互独立的。例如,如果你知道溶剂的化学势如何随浓度变化,你就可以通过这个方程推导出溶质的化学势如何变化。
- 理想溶液 (Ideal solution): 这是我们研究溶液时最简单的理论模型,类似于理想气体在气体研究中的地位。理想溶液的一个关键特征是它在所有浓度范围内都严格遵守拉乌尔定律 (Raoult's law)。现实中,只有分子结构和相互作用力非常相似的液体(如苯和甲苯)混合时才接近理想溶液。
3. 活度和标准态
We will also be introduced to a term called "activity" $\boldsymbol{a}_{j}$, which measures a solution's deviation from ideality or it's "effective concentration" in a mixture. Activity is calculated with respect to a specific standard state. Activity of pure substances in condensed phases (solid or liquids) is normally taken as 1. We have the freedom to choose the specific standard state depending on the physical system we are looking at. This chapter looks at two commonly used standard states:
1) A solvent (Raoult's law standard state)
2) A solute (Henry's law standard state)
详细解释
这部分引入了活度这个重要概念,用以修正非理想行为。
- 活度 (aj): 在理想溶液中,我们可以直接使用摩尔分数(浓度)来计算其化学势等热力学性质。但在真实溶液中,分子间的相互作用力(吸引或排斥)使得其行为偏离理想状态。活度就是对浓度的一种修正,可以被看作是组分在混合物中的“有效浓度”或“表观浓度”。它将真实溶液的复杂行为,用一个简单的、类似于理想溶液的数学形式来表达。
- 偏离理想性的度量: 如果一个组分的活度等于其摩尔分数 (aj=xj),那么它在该条件下表现为理想行为。如果 aj=xj,则表示存在偏离。
- 标准态 (Standard State): 活度是一个相对值,它的计算必须基于一个参考点,这个参考点就是标准态。在标准态下,组分的活度定义为1。选择不同的标准态,活度的数值也会不同。
- 纯凝聚相的活度: 对于纯的固体或液体(凝聚相),其标准态通常就定义为它自身在特定温度和压力(通常是1 bar)下的状态。因此,纯固体或纯液体的活度通常取为1。
- 两种常用的标准态:
- 溶剂 (Solvent): 对于溶液中占主导地位的组分(溶剂),我们通常使用基于拉乌尔定律的标准态。这个标准态是纯的溶剂。当溶剂的摩尔分数 xsolvent→1 时,其行为接近理想,遵循拉乌尔定律。
- 溶质 (Solute): 对于溶液中含量较少的组分(溶质),我们通常使用基于亨利定律的标准态。这个标准态是一个假想的状态,即溶质在摩尔分数为1,但其环境仍然像在无限稀释溶液中一样。当溶质的摩尔分数 xsolute→0 时,其行为遵循亨利定律。
4. 拉乌尔定律与亨利定律
Pj=xjPj∗
Pj=xjkH,j
详细解释
这里给出了两个描述溶液蒸气压的基本定律的数学表达式。
-
拉乌尔定律 (Raoult's Law):
Pj=xjPj∗
- Pj 是组分 j 在溶液上方的分蒸气压。
- xj 是组分 j 在液相中的摩尔分数。
- Pj∗ 是纯组分 j 在相同温度下的饱和蒸气压。这是一个常数,只取决于温度和物质种类。
- 物理意义: 该定律指出,在理想溶液中,某个组分的分蒸气压与其在液相中的摩尔分数成正比。你加入的越多,它挥发出来的也就越多。这一定律非常适用于描述溶剂的行为,尤其是在溶质浓度很低时。
- 数值示例: 假设在20°C时,纯苯(PB∗)的蒸气压是10 kPa,纯甲苯(PT∗)的蒸气压是3 kPa。如果我们将0.8摩尔的苯和0.2摩尔的甲苯混合形成一个理想溶液,那么苯在液相中的摩尔分数 xB=0.8/(0.8+0.2)=0.8。根据拉乌尔定律,苯的分蒸气压将是 PB=0.8×10 kPa=8 kPa。
-
亨利定律 (Henry's Law):
Pj=xjkH,j
- Pj 和 xj 的定义同上。
- kH,j 是组分 j 在特定溶剂中的亨利常数。这个常数取决于溶质、溶剂和温度。
- 物理意义: 该定律指出,在稀溶液中,溶质的分蒸气压与其在液相中的摩尔分数成正比。它通常用于描述溶质的行为。注意,亨利常数 kH,j 通常不等于纯溶质的蒸气压 Pj∗。
- 数值示例: 假设氧气在水中的亨利常数 kH,O2 在25°C时约为 4.4×104 bar。如果水中的氧气摩尔分数为 xO2=2×10−5,那么根据亨利定律,液面上方氧气的分压将是 PO2=(2×10−5)×(4.4×104 bar)=0.88 bar。
5. 理想溶液的性质与相图
An ideal solution follows Raoult's law across the range of concentrations. Additionally, $\Delta H_{\text {mix }}=0$ and $\Delta V_{\text {mix }}=0$.
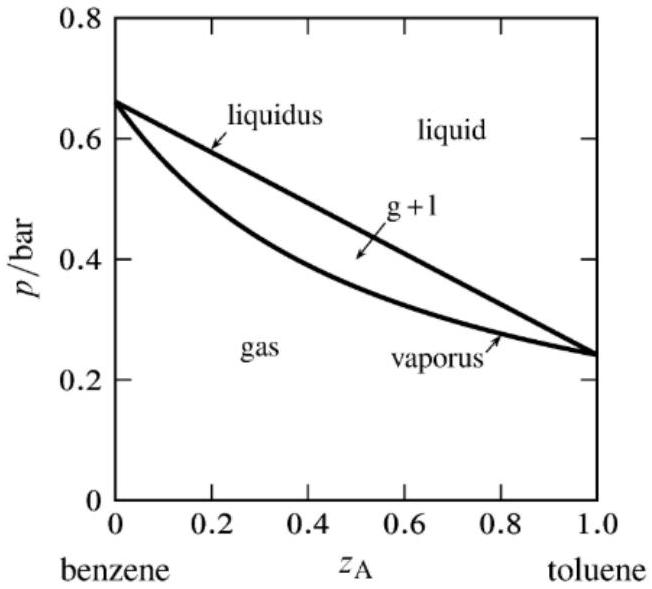
The solution of toluene (A) in a mixture with benzene (B) is close to ideal and follows Raoult's law in the two-phase equilibrium region $\mathbf{g}+\mathbf{l}$.
Here, $\mathrm{z}_{\mathrm{A}}$ is the mole fraction of toluene in the composition.
You will also see variables $\mathbf{x}_{\mathbf{A}}$ and $\mathbf{y}_{\mathbf{A}}$ which are the mole fraction of toluene in the liquid phase and the vapor phase, respectively. It should be evident that
$$
p_{\mathrm{A}}=x_{\mathrm{A}} p_{\mathrm{A}}^{*} \quad p_{\mathrm{B}}=\left(1-x_{\mathrm{A}}\right) p_{\mathrm{B}}^{*}
$$
Additionally, at equilibrium between gas and liquid phases $\mathbf{g}+\mathbf{l}, \mu_{A}^{l}\left(T, P, x_{A}\right)=\mu_{A}^{g}\left(T, P, y_{A}\right)$.
Vaporus: Also called "dew point line" or "saturated vapor line," it is the point of formation of the first liquid drop as you increase pressure.
Liquidus: Also called "bubble point line" or "saturated liquid line," it is the point of formation of first vapor bubble as pressure decreases.
详细解释
这部分详细描述了理想溶液的宏观性质,并结合一个典型的压力-组成相图进行说明。
-
理想溶液的宏观性质:
- 混合焓变 (Enthalpy of Mixing) ΔHmix=0: 这意味着混合过程不放热也不吸热。其微观解释是,不同种类的分子(A-B)之间的作用力与同种类的分子(A-A, B-B)之间的作用力完全相同。
- 混合体积变 (Volume of Mixing) ΔVmix=0: 这意味着混合后的总体积恰好等于混合前各组分体积之和。例如,混合50 mL的组分A和50 mL的组分B,得到的溶液体积正好是100 mL。
-
压力-组成相图 (Pressure-Composition Phase Diagram):
- 坐标轴: 纵轴是总压力 (P),横轴是体系的总组成,用甲苯的摩尔分数 zA 表示。
- 体系: 苯(B)和甲苯(A)的二元混合物。这是一个经典的近乎理想的溶液体系,因为苯和甲苯分子结构相似,相互作用力也相近。
- 区域划分:
- 上部区域 (l): 标记为 "l",代表液相 (liquid)。在此区域的高压下,整个体系以单一的液相存在。
- 下部区域 (g): 标记为 "g",代表气相 (gas/vapor)。在此区域的低压下,整个体系以单一的气相存在。
- 中间纺锤形区域 (g + l): 这是气液两相共存的平衡区域。在此区域内,体系会分离成一个液相和一个气相,它们处于动态平衡中。
- 变量区分:
- zA: 体系的总摩尔分数,代表加入的甲苯的总量占总摩尔数的比例。
- xA: 在气液共存区,液相 (liquid phase) 中甲苯的摩尔分数。
- yA: 在气液共存区,气相 (vapor phase) 中甲苯的摩尔分数。
- 相图中的线:
- 液相线 (Liquidus): 上方的曲线,也叫泡点线 (bubble point line)。它表示在给定组成下,液相开始沸腾(出现第一个气泡)的压力。从液相区降低压力,当压力触及这条线时,开始有气体生成。
- 气相线 (Vaporus): 下方的曲线,也叫露点线 (dew point line)。它表示在给定组成下,气相开始冷凝(出现第一滴液体)的压力。从气相区增加压力,当压力触及这条线时,开始有液体生成。
- 平衡条件: 在气液共存区,两相达到平衡的热力学判据是,任意组分(如A)在液相中的化学势 (μAl) 必须等于其在气相中的化学势 (μAg)。
μAl(T,P,xA)=μAg(T,P,yA)
- 拉乌尔定律的应用: 文档中给出的公式 pA=xApA∗ 和 pB=(1−xA)pB∗ 是对这个理想体系中每个组分分压的描述。注意 xB=1−xA。
6. 问题1:推导气相线方程
When the binary system contains a liquid phase and a gas phase in equilibrium, the total pressure is the sum of $\mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{A}}$ and $\mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{B}}$
$$
\begin{equation*}
P_{\text {total }}=x_{A} P_{A}^{*}+x_{B} P_{B}^{*} \tag{1}
\end{equation*}
$$
and the vapor phase fraction of benzene can be defined as
$$
\begin{equation*}
y_{B}=\frac{x_{B} P_{B}^{*}}{P_{\text {total }}} \tag{2}
\end{equation*}
$$
1.) Derive equation 3, which is the vaporus line in the above figure.
...
$$
\begin{equation*}
P_{\text {total }}=\frac{P_{A}^{*} P_{B}^{*}}{P_{B}^{*}-y_{B}\left(P_{B}^{*}-P_{A}^{*}\right)} \tag{3}
\end{equation*}
$$
详细解释与推导
这个问题的目标是推导出**气相线(Vaporus line)**的方程。气相线方程描述了总压力 Ptotal 和气相组成 (yA 或 yB) 之间的关系。我们手上有两个基本关系:
- 总压是液相组成 xA,xB 的函数(这是液相线方程)。
- 气相组成 yB 和液相组成 xB 之间的关系(道尔顿分压定律和拉乌尔定律的结合)。
我们的任务是消去中间变量 xA 和 xB,得到一个只包含 Ptotal 和 yB 的关系。
推导步骤: (我们以苯,即组分B为例进行推导)
-
第一步: 改写方程(1)
根据题目提示,将 xA 替换为 1−xB。
Ptotal=(1−xB)PA∗+xBPB∗
整理后得到:
Ptotal=PA∗−xBPA∗+xBPB∗
Ptotal=PA∗+xB(PB∗−PA∗)(∗)
这个方程是总压 Ptotal 与液相组成 xB 的关系,它本身就是液相线的方程(如果横坐标是 xB 的话)。
-
第二步: 从方程(2)中解出 xB
方程(2)是 yB=PtotalxBPB∗。我们可以从中解出 xB:
xB=PB∗yBPtotal(∗∗)
-
第三步: 将 xB 的表达式代入改写后的方程(1)中
将表达式 (**) 代入方程 (*),以消去 xB:
Ptotal=PA∗+(PB∗yBPtotal)(PB∗−PA∗)
-
第四步: 求解 Ptotal
我们的目标是得到一个 Ptotal=f(yB) 的表达式。所以我们需要把所有含 Ptotal 的项移到一边。
Ptotal−(PB∗yBPtotal)(PB∗−PA∗)=PA∗
提取公因式 Ptotal:
Ptotal[1−PB∗yB(PB∗−PA∗)]=PA∗
将方括号内的项通分:
Ptotal[PB∗PB∗−yB(PB∗−PA∗)]=PA∗
现在,将 Ptotal 分离出来:
Ptotal=PB∗−yB(PB∗−PA∗)PA∗PB∗
这就是我们要推导的方程(3)。这个方程直接关联了系统的总压力 Ptotal 和气相的组成 yB,因此它定义了气相线。
7. 偏摩尔量 (Partial molar quantities) (24-1)
We're starting to use our total differentials and Maxwell relations to describe actual physical systems. In this unit we'll mostly use Gibbs energy for its dependence on $T$ and $P$, which are easily measured experimental quantities. Recall our total derivatives for $G$:
...
详细解释
这部分开始从数学上引入描述多组分体系性质的工具——偏摩尔量,特别是化学势。
-
吉布斯自由能 (Gibbs Energy, G): 选用吉布斯自由能是因为它的自然变量是温度 T 和压力 P,这正是实验中最容易控制和测量的两个宏观量。
-
G 的全微分 (Total Differential of G):
对于一个组成固定的封闭系统(即 ni 恒定),吉布斯自由能的全微分是:
dG=(∂T∂G)P,ndT+(∂P∂G)T,ndP=−SdT+VdP
这里 (∂T∂G)P,n=−S 和 (∂P∂G)T,n=V 是重要的麦克斯韦关系。
-
推广到多组分开放系统:
当体系中有多种组分,并且每种组分的摩尔数 nj 可以变化时(比如在化学反应中,或者向体系中添加物质),我们需要在 dG 的表达式中加入这些变量的影响。
G=G(T,P,n1,n2,n3,…)
其全微分就变成了:
dG=(∂T∂G)P,{nj}dT+(∂P∂G)T,{nj}dP+i∑(∂ni∂G)T,P,nj=idni
将麦克斯韦关系和化学势的定义代入,得到基本方程:
dG=−SdT+VdP+i∑μidni
-
化学势 (μj) 的定义:
μj=(∂nj∂G)T,P,ni=j
- 物理意义: 化学势 μj 表示在恒温、恒压下,向一个大体系中加入1摩尔组分 j 时,体系吉布斯自由能的增量。下标 ni=j 表示在求偏导数时,所有其他组分的摩尔数都保持不变。化学势是物质发生化学反应或相变的驱动力,物质总是倾向于从化学势高的地方移动到化学势低的地方。
-
偏摩尔吉布斯自由能 (Gˉj):
文档指出 μj=Gˉj。这是一个非常重要的等价关系。偏摩尔量 Yˉj 是一个广义的概念,定义为:
Yˉj=(∂nj∂Y)T,P,ni=j
其中 Y 可以是任何广延性质,如体积 V、焓 H、熵 S 等。
- Gˉj 就是偏摩尔吉布斯自由能。
- Vˉj 就是偏摩尔体积,表示在恒温恒压下,加入1摩尔组分 j 引起的体系总体积的变化。
-
偏摩尔量是强度性质: 虽然偏摩尔量是从广延性质(如G, V)求导得来的,但它本身是一个强度性质,不依赖于体系的大小。
8. 二元溶液和广延性质的积分形式
An example of a 2-component system is called a binary solution...
dG = -SdT + VdP + \mu_1 dn_1 + \mu_2 dn_2
... at constant T and P,
dG = \mu_1 dn_1 + \mu_2 dn_2
... integrate to obtain:
G(T, P, n_1, n_2) = \mu_1 n_1 + \mu_2 n_2
... for a single (pure) component system, $G = \mu n$, or $\mu = G/n = \bar{G}$.
In your homework it is useful to use partial molar volumes...
V(T, P, n_1, n_2) = \bar{V}_1 n_1 + \bar{V}_2 n_2
详细解释
这部分展示了如何从偏摩尔量的微分形式得到其积分形式,这对计算体系的总性质至关重要。
-
恒温恒压下的吉布斯自由能: 在 T 和 P 恒定时,dT=0,dP=0,所以 dG 的表达式简化为:
dGT,P=μ1dn1+μ2dn2
-
积分得到总吉布斯自由能:
文档中提到的“McQuarrie的技巧”是基于欧拉齐次函数定理。一个简化的理解是:想象我们有一个确定组成的溶液(即 μ1 和 μ2 是定值),我们将其体积(以及摩尔数)从0“放大”到最终的 n1 和 n2。在这个过程中,我们将上式积分:
∫0GdG=∫0n1μ1dn1′+∫0n2μ2dn2′
因为在放大过程中比例不变,所以 μ1 和 μ2 是常数,可以提到积分号外:
G=μ1∫0n1dn1′+μ2∫0n2dn2′
最终得到:
G(T,P,n1,n2)=n1μ1+n2μ2
这个公式非常重要,它表明体系的总吉布斯自由能等于各组分的摩尔数乘以其各自的化学势之和。
-
推广到其他偏摩尔量:
这个关系可以推广到任何广延性质 Y:
Y(T,P,n1,n2)=n1Yˉ1+n2Yˉ2
例如,对于体积 V:
V(T,P,n1,n2)=n1Vˉ1+n2Vˉ2
- 数值示例 (1-丙醇和水): 文档提到1-丙醇和水的混合。这是一个典型的非理想溶液,其 ΔVmix=0。假设在25°C,水的摩尔体积 Vm(H2O) 约为 18 cm³/mol,1-丙醇的摩尔体积 Vm(PrOH) 约为 75 cm³/mol。
- 如果我们混合1摩尔水(18 cm³)和1摩尔1-丙醇(75 cm³),理想情况下总体积应为 18+75=93 cm³。
- 但实际上,由于水和丙醇分子间的氢键作用,它们会“挤”得更紧密,导致实际总体积可能只有约 91 cm³。
- 这意味着 ΔVmix=91−93=−2 cm³。在这个混合溶液中,水的偏摩尔体积 VˉH2O 和1-丙醇的偏摩尔体积 VˉPrOH 都不再等于它们纯液体时的摩尔体积。
9. 吉布斯-杜亥姆关系 (Gibbs-Duhem Relation) (24-2)
2.) Derivation of Gibbs-Duhem Relation
a. At constant T and P, we can write G(T, P, n_1, n_2) = \mu_1 n_1 + \mu_2 n_2. Differentiate both sides.
b. We also know that at constant T and P, we have dG = \mu_1 dn_1 + \mu_2 dn_2. Subtract this from the expression in (a). What does this leave us?
c. Let's divide both sides by (n_1 + n_2). What is the definition of mole fraction? Qualitatively, what does this final expression tell us?
详细解释与推导
这个问题引导我们推导吉布斯-杜亥姆方程,它展示了多组分体系中各组分化学势之间的制约关系。
-
a. 对积分形式求全微分:
我们从 G=n1μ1+n2μ2 开始。使用乘法法则对其求全微分。注意,n1,n2,μ1,μ2 都可能变化。
dG=(n1dμ1+μ1dn1)+(n2dμ2+μ2dn2)
整理一下:
dG=n1dμ1+n2dμ2+μ1dn1+μ2dn2(Eq.A)
-
b. 减去基本方程:
我们已知在恒温恒压下,dG 的基本表达式是:
dG=μ1dn1+μ2dn2(Eq.B)
现在用 (Eq. A) 减去 (Eq. B):
(n1dμ1+n2dμ2+μ1dn1+μ2dn2)−(μ1dn1+μ2dn2)=0
消去相同项后,我们得到:
n1dμ1+n2dμ2=0
这就是吉布斯-杜亥姆方程在恒温恒压下的形式。
-
c. 除以总摩尔数并解释:
将上式两边同时除以总摩尔数 ntotal=n1+n2:
n1+n2n1dμ1+n1+n2n2dμ2=0
根据摩尔分数 (mole fraction) 的定义,x1=n1+n2n1 和 x2=n1+n2n2。代入后得到最终形式:
x1dμ1+x2dμ2=0
定性解释: 这个方程告诉我们,在一个二元溶液中,两种组分的化学势的变化不是独立的。如果一个组分的化学势因为浓度的改变而增加 (dμ1>0),那么另一个组分的化学势必须减小 (dμ2<0),以保持方程成立。这体现了体系内部的一种制衡关系。
10. 问题3:理想溶液化学势方程的推导
3.) The chemical potential of an ideal solution can be written as:
$$
\mu_{1}=\mu_{1}^{*}+R T \ln \left(x_{1}\right)
$$
where $\mu_{1}{ }^{*}$ is the chemical potential of the pure solvent and $\mathrm{x}_{1}$ is its mole fraction. Derive this equation and show all steps of work.
详细解释与推导
这个问题的目标是推导理想溶液中组分化学势的表达式。
-
a. 定义理想溶液和使用的定律:
理想溶液是指其蒸气严格遵守拉乌尔定律的溶液。拉乌尔定律 P1=x1P1∗ 是这个推导的关键。
-
b. 使用吉布斯自由能的微分形式:
对于纯物质或混合物中的单一组分,在恒温下,其化学势(即摩尔吉布斯自由能)随压力的变化关系为:
dμ1=Vˉ1dP
这里 Vˉ1 是组分1的偏摩尔体积。
-
c. 引入理想气体假设并积分:
我们考虑液相和气相处于平衡状态。气相中的组分1可以近似看作理想气体,其摩尔体积为 Vˉ1=Vm=P1RT。将此代入上式:
dμ1=P1RTdP1
现在,我们对这个微分方程进行积分。积分的下限是标准态,上限是当前状态。
- 标准态: 纯液体1,其化学势为 μ1∗,其蒸气压为 P1∗。
- 当前状态: 溶液中的组分1,其化学势为 μ1,其分蒸气压为 P1。
∫μ1∗μ1dμ1′=∫P1∗P1RTP1′dP1′
积分得到:
μ1−μ1∗=RT[ln(P1)]P1∗P1
μ1−μ1∗=RT(lnP1−lnP1∗)
利用对数运算法则 lna−lnb=ln(a/b):
μ1=μ1∗+RTln(P1∗P1)
(注意:文档中的 μ1∘ 和 P1∘ 在这里对应 μ1∗ 和 P1∗,即纯液体标准态。)
-
d. 应用拉乌尔定律:
对于理想溶液,我们有拉乌尔定律: P1=x1P1∗。
所以,P1∗P1=x1。
将此关系代入上式:
μ1=μ1∗+RTln(x1)
-
e. 最终形式:
这正是我们要推导的方程(4)。μ1∗ 是纯溶剂的化学势,是标准态化学势。这个方程定量地描述了将纯溶剂混合成理想溶液后,其化学势会如何因为浓度的变化而降低(因为 x1≤1,所以 ln(x1)≤0)。
11. 练习题4:应用吉布斯-杜亥姆方程
4.) For example, suppose we had a liquid-liquid solution, and we were to know that the chemical potential of component 2:
$$
\mu_{2}=\mu_{2}^{*}+R T \ln x_{2} \quad for \quad 0 \leq x_{2} \leq 1
$$
How can we use the Gibbs-Duhem relation to find the equation $\mu_{1}$ ?
详细解释与求解
这个问题展示了吉布斯-杜亥姆方程的威力:已知一个组分的化学势表达式,可以求出另一个组分的。
-
a. 对 μ2 求微分:
给定的表达式是 μ2=μ2∗+RTlnx2。我们对它求微分,得到 dμ2。注意 μ2∗ 和 RT 是常数。
dμ2=d(μ2∗+RTlnx2)=RT⋅d(lnx2)=RTx21dx2
-
b. 代入吉布斯-杜亥姆方程:
吉布斯-杜亥姆方程是 x1dμ1+x2dμ2=0。
将 dμ2 的表达式代入:
x1dμ1+x2(RTx21dx2)=0
简化后得到:
x1dμ1+RTdx2=0
-
c. 利用摩尔分数关系进行替换:
我们知道 x1+x2=1。对这个关系式求微分,得到 d(x1+x2)=d(1),即:
dx1+dx2=0⟹dx2=−dx1
将这个关系代入上一步的方程中:
x1dμ1+RT(−dx1)=0
x1dμ1=RTdx1
dμ1=RTx1dx1
-
d. 积分求 μ1:
现在我们对上式进行积分来求 μ1。
∫dμ1=∫RTx1dx1
积分结果为:
μ1=RTlnx1+C
其中 C 是积分常数。为了确定 C,我们需要一个边界条件。当溶液为纯组分1时,x1=1,此时其化学势应为纯组分1的化学势 μ1∗。
代入 x1=1:
μ1∗=RTln(1)+C
因为 ln(1)=0,所以 C=μ1∗。
将积分常数代回,我们得到 μ1 的最终表达式:
μ1=μ1∗+RTlnx1
这个结果表明,如果组分2在所有浓度范围内都表现出理想行为,那么组分1也必须表现出理想行为。
12. 练习题5:处理非理想溶液的蒸气压数据
5.) The vapor pressure (in torr) of the two components in a binary solution are given by
$$
P_{1}=120 x_{1} e^{0.20 x_{2}^{2}+0.10 x_{2}^{3}}
$$
And
$$
P_{2}=140 x_{2} e^{0.35 x_{1}^{2}-0.10 x_{1}^{3}}
$$
Determine the values of $P_{1}^{*}, P_{2}^{*}, k_{H, 1}$ and $k_{H, 2}$.
详细解释与求解
这个问题给出了一个非理想溶液的蒸气压模型(因为表达式中含有指数项,偏离了拉乌尔定律),要求我们根据这个模型确定四个关键参数。
-
求解 P1∗ (纯组分1的饱和蒸气压):
P1∗ 的定义是当体系中只含有纯组分1时的蒸气压。此时,x1=1 且 x2=0。
我们将这些值代入 P1 的表达式:
P1∗=120⋅(1)⋅e0.20⋅(0)2+0.10⋅(0)3
P1∗=120⋅e0=120⋅1=120 torr
-
求解 P2∗ (纯组分2的饱和蒸气压):
P2∗ 的定义是当体系中只含有纯组分2时的蒸气压。此时,x2=1 且 x1=0。
我们将这些值代入 P2 的表达式:
P2∗=140⋅(1)⋅e0.35⋅(0)2−0.10⋅(0)3
P2∗=140⋅e0=140⋅1=140 torr
-
求解 kH,1 (组分1作为溶质时的亨利常数):
亨利定律描述的是溶质在极稀溶液中的行为,即 x1→0。根据亨利定律的定义 P1=kH,1x1,我们可以得到 kH,1=limx1→0x1P1。
当 x1→0 时,x2→1。
kH,1=x1→0limx1120x1e0.20x22+0.10x23
kH,1=x2→1lim120⋅e0.20x22+0.10x23
现在代入 x2=1:
kH,1=120⋅e0.20⋅(1)2+0.10⋅(1)3=120⋅e0.20+0.10=120⋅e0.30
计算数值: e0.30≈1.34986
kH,1≈120×1.34986≈161.98 torr
-
求解 kH,2 (组分2作为溶质时的亨利常数):
同理,当组分2是溶质时,x2→0 且 x1→1。
kH,2=x2→0limx2P2=x2→0limx2140x2e0.35x12−0.10x13
kH,2=x1→1lim140⋅e0.35x12−0.10x13
现在代入 x1=1:
kH,2=140⋅e0.35⋅(1)2−0.10⋅(1)3=140⋅e0.35−0.10=140⋅e0.25
计算数值: e0.25≈1.2840
kH,2≈140×1.2840≈179.76 torr
这份文档的全面解析到此结束。希望能帮助您彻底理解其中的所有内容。